Jasmine sambac
Scientific name|Jasminum sambac
Origin|China
Classification|Flower series
Specifications|500g-25kg Please contact sales for details
Extraction part|Flower
Extraction method | Abs.
Plant family|Oleaceae
Aroma|Combination of honey tea, and rich floral scent
▎Essential Oil Introduction
Jasmine Sambac essential oil originates from the moist and fertile, slightly acidic sandy soil of India. It thrives in a tropical monsoon climate characterized by year-round high temperatures and acidic soil predominance. Jasmine Sambac prefers slightly acidic sandy soil, is intolerant to cold, and can be grown in full or partial sunlight, with a flowering period from June to September. During the mid-flowering stage, when the buds are about to bloom into a "tiger claw" shape, they are harvested at around three or four in the afternoon to maximize fragrance and oil yield. This variety is common in India and is also known as "Forest Moonlight."
Jasmine comes in various varieties, so it's important to pay attention to the specific variety when choosing jasmine essential oil. Common varieties found in essential oils include Moroccan Jasmine (Jasminum grandiflorum), Star Jasmine (Jasminum auriculatum), and Arabian Jasmine (Jasminum sambac). The original essence is obtained through solvent extraction.
Arabian Jasmine emits a serene and lofty fragrance with bright tones, offering an endless flow of refreshing energy. Blooming with a fragrant scent at night, Arabian Jasmine evokes the mysterious ambiance of moonlight, carrying a subtle energy and radiating gentle feminine charm. It is an excellent choice for women, embodying soft and soothing allure.
▎Component Analysis
|Main Component:Indole, Cis-Jasmone, α-Farnesene
The indole component in Jasmine Sambac essential oil helps enhance charm, while Cis-Jasmone regulates oil secretion, bringing a sense of ease and tranquility. α-Farnesene is responsible for a special sweet and clear fragrance, detectable at the beginning of blooming. However, this structure is easily destroyed by light and heat, hence the reason for harvesting it in the early morning to avoid sun damage to the flower's fragrance.
Its components include α-Farnesene, Indole (with a content of up to 14%), (S)(-)-Linalool (up to 15%), Methyl Anthranilate (5%), Benzyl acetate (4-5%), Phenylethanol (2-3%), Jasminelac-tone, and other components.
|Component 1:Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C8H7N. It features a double-ring structure composed of a five-membered pyrrole ring fused with a six-membered benzene ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by various bacteria, serving as a signaling molecule between cells.
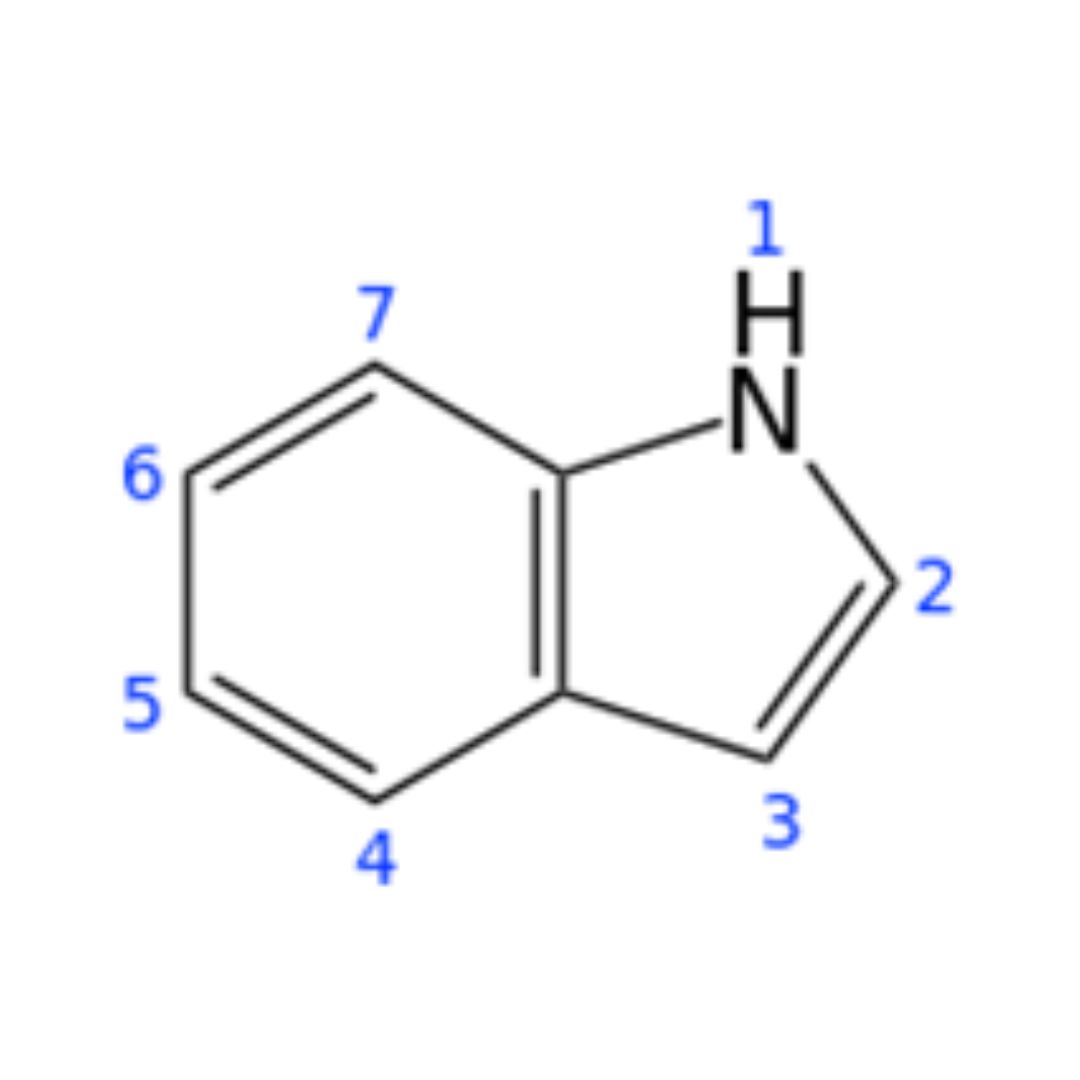
▸ Indole derivatives play important cellular roles in regulating various aspects of bacterial physiology (including sporulation, plasmid stability, drug resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence). These derivatives also include neurotransmitters, such as serotonin.
|Component 2:Cis-Jasmone
Arabian Jasmine contains a high content of cis-jasmone. Cis-jasmone exists in two isomeric forms: cis and trans. In nature, only the cis isomer is found, while the trans isomer can only be synthetically produced. Cis-jasmone is a gentle ingredient that adds a luxurious feel and enhances charm, leaving one feeling refreshed and uplifted.

▸ There are studies related to the chemical composition of jasmine extract on blood vessels.
|Raw Material Certifications
To obtain relevant certification information, please contact us on WhatsApp.
▎References
- Lee, Jin-Hyung; Lee, Jintae (2010). "Indoleas an intercellular signal in microbial communities". FEMSMicrobiology Reviews. 34 (4): 426–44.
- Baeyer, A.; Emmerling, A.(1869). "Synthese des Indols" [Synthesis ofindole]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 2: 679–682.
- Wikoff WR, Anfora AT, Liu J,Schultz PG, Lesley SA, Peters EC, Siuzdak G (March 2009). "Metabolomics analysisreveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites". Proc.Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 (10): 3698–3703.
- Ali Esmail Al-Snafi(2018). "Pharmacological and Therapeutic Effects of Jasminumsambac - A Review". Indo Am. J. P. Sci. 05 (3).
- Santhanam, Jacinta; Ghani, Farhana Nadiah Abd; Basri, Dayang Fredalina (2014). "Antifungal Activity of Jasminum sambac against Malassezia sp. and Non-Malassezia sp. Isolated from Human Skin Samples". Journal of Mycology. 2014: 1–7.
- Braun NA, Kohlenberg B, Sim S, Meier M, Hammerschmidt FJ. Jasminum flexile flower absolute from India--a detailed comparison with three other jasmine absolutes. Nat Prod Commun. 2009 Sep;4(9):1239-50.
- Phanukit Kunhachan et al. Chemical Composition, Toxicity and Vasodilatation Effect of the Flowers Extract of Jasminum sambac (L.) Ait. “G. Duke of Tuscany”. March 2012.Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative. Medicine 2012(4):471312
- Kanlayavattanakul M, Kitsiripaisarn S, Lourith N. Aroma profiles and preferences of Jasminum sambac L. flowers grown in Thailand. J Cosmet Sci. 2013 Nov-Dec;64(6):483-93.
- Braun NA, Sim S.Jasminum sambac flower absolutes from India and China--geographic variations. Nat Prod Commun. 2012 May;7(5):645-50.
|Some images sourced from the internet. Contact for copyright removal|