▎Essential Oil Introduction
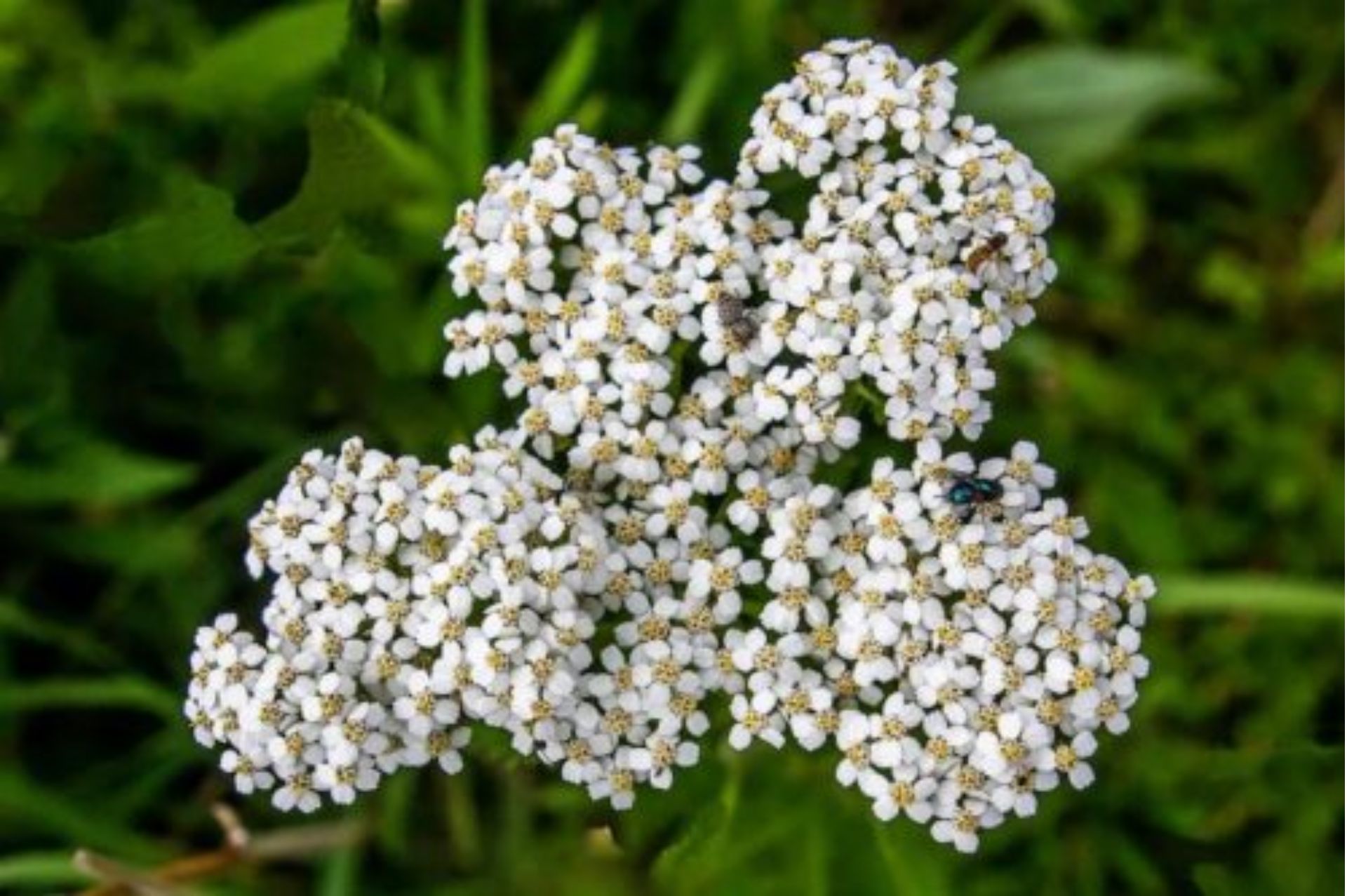
Yarrow essential oil is originates from Pécs, one of the ancient cities in Hungary. It is located between the Danube and Drava rivers. It has a pleasant climate, long sunshine hours throughout the year, and a continental temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest climate. Yarrow is very cold-tolerant and grows in hillside grasslands. It prefers an environment with sufficient sunshine and well-drained soil.
Yarrow is a large perennial herb with dark green leaves that emit a fragrant aroma. Its surface looks like lace or feathers. Its species name millefolium means "thousand leaves", with mini-shaped flowers that bloom in flower heads, is a very ancient and important medicinal herb.
The Latin name comes from Achilles in Greek mythology. It is said that yarrow was Achilles' healing herb on the battlefield. In the classical period, it received the nickname "Herba Militaris", which means "battlefield herb". Also often used as a substitute for German chamomile.
▎Component Analysis
▎Main Components: Monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, ketones, oxides
Yarrow (Achilea millefolium) essential oil is obtained through steam distillation, and its composition includes monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, ketones, and oxides. The primary constituents are chamazulene, beta-caryophyllene, alpha- and beta-pinene, sabinene, linalool, 1,8-cineole, bornyl acetate, camphor, borneol, and more.

▸ The pharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of Yarrow (Achillea millefolium). Commonly used to treat gastrointestinal discomfort, hepatobiliary, and gynecological conditions.

▸ Yarrow hydroxyethanol extract: It is an effective ingredient for cosmetics and has great potential to improve the effectiveness of cosmetic ingredients.
|Component 1: Chamazulene
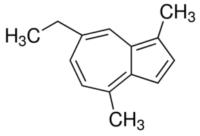
▸ Azulene is a blue substance formed during the distillation process. Chamazulene is derived from azulene.

▸ In vitro and in vivo models have shown that Chamazulene reverses arthritis inflammation by regulating matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and the NF-kβ pathway.
|Component 2: Sabinene
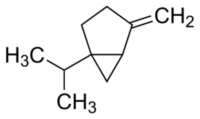
▸ Sabinene chemical structure.
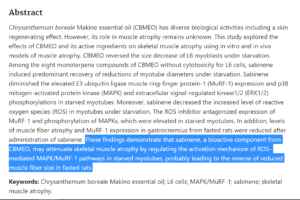
▸ In research, it was found that sabinene has related research on skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating the MAPK-MuRF-1 pathway in rats.
|Component 3: beta-caryophyllene
▸ beta-caryophyllene chemical structure.

▸ β-Caryophyllene has been studied to help wound recovery through various pathways.
▎Raw Material Certifications
To obtain relevant certification information, please contact us on WhatsApp.
▎References
- Ding Ma , Jinlong He , Dapeng He. Chamazulene reverses osteoarthritic inflammation through regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and NF-kβ pathway in in-vitro and in-vivo models. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020 Feb;84(2): 402-410.
- Rezaei S, Ashkar F, Koohpeyma F, Mahmoodi M, Gholamalizadeh M, Mazloom Z, Doaei S. Hydroalcoholic extract of Achillea millefolium improved blood glucose, liver enzymes and lipid profile compared to metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Lipids Health Dis . 2020 Apr 27;19(1):81.
- Gaweł-Bęben K, Strzępek-Gomółka M, Czop M, Sakipova Z, Głowniak K, Kukula-Koch W. Achillea millefolium L. and Achillea biebersteinii Afan. Hydroglycolic Extracts-Bioactive Ingredients for Cosmetic Use.Molecules. 2020 Jul 24; 25(15):3368.
- Yunkyoung Ryu et al. Sabinene Prevents Skeletal Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting the MAPK-MuRF-1 Pathway in Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4955.
- Ayoobi F, Moghadam-Ahmadi A, Amiri H, Vakilian A, Heidari M, Farahmand H, Fathollahi MS, Fatemi I, Shafiei SA, Alahtavakoli M, Shamsizadeh A. Achillea millefolium is beneficial as an add-on therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:89-97.
- Sachiko Koyama et al. Beta-caryophyllene enhances wound healing through multiple routes, PLoS One. 2019 Dec 16;14(12):e0216104.
- Ali SI, Gopalakrishnan B, Venkatesalu V. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Properties of Achillea millefolium L.: A Review. Phytother Res. 2017 Aug;31(8):1140-1161.
- García-Risco MR, Mouhid L, Salas-Pérez L, López-Padilla A, Santoyo S, Jaime L, Ramírez de Molina A, Reglero G, Fornari T. Biological Activities of Asteraceae (Achillea millefolium and Calendula officinalis) and Lamiaceae (Melissa officinalis and Origanum majorana) Plant Extracts. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2017 Mar;72(1):96-102.
- Becker LC, Bergfeld WF, Belsito DV, Hill RA, Klaassen CD, Liebler DC, Marks JG Jr, Shank RC, Slaga TJ, Snyder PW, Andersen FA.Safety Assessment of Achillea millefolium as Used in Cosmetics. Int J Toxicol. 2016 Nov;35(3 suppl):5S-15S.
- Akram M.Minireview on Achillea millefolium Linn. J Membr Biol. 2013 Sep;246(9):661-3.
|Some images sourced from the internet. Contact for copyright removal|