Copaiba balsam
Scientific name|Copaifera langsdorfii
Origin|Brazil
Classification|Resin series
Specifications|500g-25kg Please contact sales for details
Extraction part|Resin
Extraction method | Distillation
Plant family|Fabaceae
Aroma|Extremely subtle, also referred to as a glass-like fragrance
▎Essential Oil Introduction
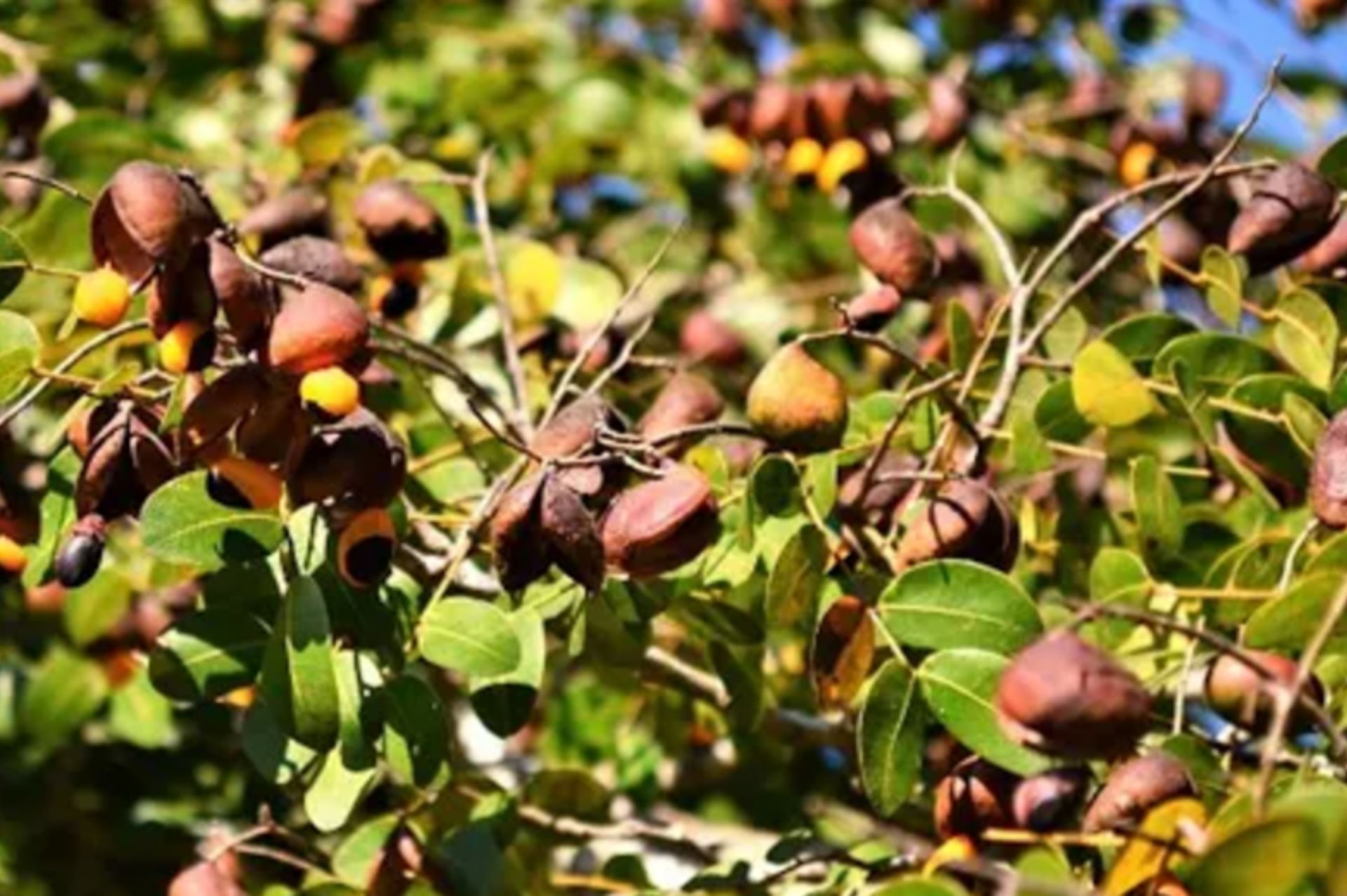
Copaiba Balsam, scientifically named Copaifera langsdorffii, belongs to the Fabaceae family and is native to the Amazon rainforest of South America. This tropical tree can grow up to 18 meters tall and has been naturally thriving in Cuba's ancient tribes for thousands of years. It holds significant value as an aromatic resin for the Indigenous peoples of Latin America. The tree is also nicknamed the "deposit tree" because slitting the bark allows resin to flow into a container. Once the container is full, it can be sold for profit.
Copaiba trees produce abundant resin, which, after filtration, can be used as lamp oil or diesel fuel, earning it the alternative name "diesel tree." Copaiba balsam has an extremely subtle aroma, often referred to as a glass-like fragrance. Its resinous properties ensure excellent longevity in its scent profile.
The harvesting of Copaiba balsam dates back to the 16th century among Indigenous tribes in northern and northeastern Brazil. In traditional medicine, the resin was used orally or applied as an ointment. The Yaviza people of Panama combined it with honey for consumption.
In the perfume industry, Copaiba balsam is widely used as a natural fixative. It has served as a substitute for oakmoss absolute, a formerly common fixative now associated with higher risks of skin sensitization. Copaiba balsam is also widely applied in soaps, creams, lotions, perfumes, and pharmaceutical formulations, including natural diuretics and cough medicines.
▎Component Analysis
|Main component: Sesquiterpenes
Also known as the "Frankincense of South America," Copaiba balsam's main component is β-caryophyllene, along with copaene, bergamotene, and humulene. These sesquiterpenes have been recognized for their beneficial properties. Copaene and bergamotene, in particular, exhibit strong protective characteristics, which can support enhanced resilience and well-being.
|Raw Material Certifications
To obtain relevant certification information, please contact us on WhatsApp.
|Some images sourced from the internet. Contact for copyright removal|